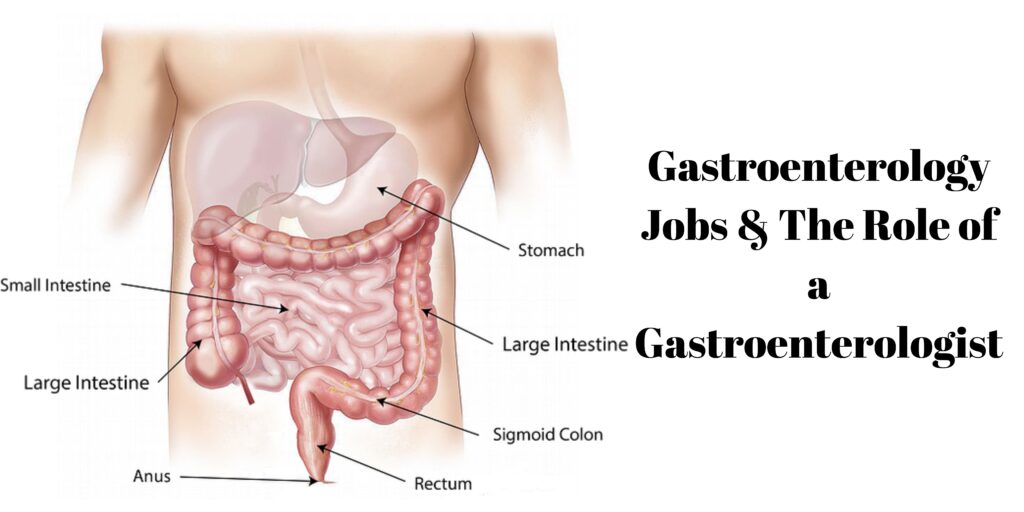
The gastroenterologist is a professional that a patient wants to see when there are issues with the belly, whether chronic pain, digestion, or bothersome symptoms like gas, bloating, or diarrhea.
These physicians are skilled in treating conditions, illnesses, or diseases of organs comprising the digestive tract. These will include the colon, esophagus, liver, stomach, pancreas. If you recognize the “telltale” symptoms start popping up, you should reach out to your GI provider.
The Gastroenterology job will be to help narrow down the problem to help get you back to right. Plus, there are preventative measures taken for high-risk patients for diseases, for example cancer of the colon. Doctors will perform regular colonoscopies.
In The Gastroenterologist’s Role, What Are Some Common Issues Dealt With
As a gastroenterologist, numerous issues can affect the organs of the digestive tract. Fortunately, because this physician specializes in this body area, the provider can offer a specific diagnosis and treat that area directly and effectively.
In many cases, an internal medicine physician will refer their patients to this subspecialist of that particular classification to get a precise diagnosis and a subsequent protocoled treatment for that specific condition.
The GI specialist sees some cases more often than others. Find out what a gastroenterologist is here.
Let us look at a few of the more common issues that come along for the provider.

- Heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation or even pain that strikes in the throat or chest. When the esophagus receives backed-up stomach acid, heartburn is the result. The esophagus connects the stomach and the mouth like a tube.
Heartburn is a relatively common condition people suffer with periodically, with it subsiding on its own or using over-the-counter meds. Persistent occasions (greater than two times each week) might be indicative of a severe problem like “GERD” or “gastroesophageal reflux disease.”
That is when the stomach acid irritates the esophagus lining, more common in overweight individuals and those who smoke.
- Gallstones
A gallbladder has the potential for forming what is described as “small, hard nuggets” referenced as gallstones. The gallbladder is a smaller organ that can be found in the belly. A gallstone has the potential for being as minute as a rice grain or as large as a golf ball. Some people will develop many stones of varied sizes, while others will only get one rather significant stone.
When you suddenly experience right-sided abdominal pain, there could be a stone. Once it moves, the pain will subside. The substances responsible for bile becoming imbalanced are accountable for these nuggets. These substances are made by the liver, referred to as digestive liquid. Physicians are uncertain why the imbalances occur.
- Lactose Intolerance
If you have dairy, whether milk or food, and it creates discomfort for you, you might be lactose intolerant. The sugar that you find in dairy is lactose. Lactase is a protein produced in the body to help dairy products break down, including yogurts and cheeses.
The reason people become lactose intolerant is that they do not produce enough lactase to digest dairy products causing them to develop belly pain, bloats, gas, diarrhea, and an upset stomach.
These signs and symptoms will usually show up roughly a couple of hours after consuming the food or beverage with mild to severe reactions. After testing a patient for the condition, the GI might recommend dietary changes and perhaps supplements.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
When the digestive tract takes in food or other substances, the immune system can mistake these items for “dangerous germs.” In error, the system turns on the healthy tissue like a malfunction causing “inflammatory bowel disease” or “IBD.”
This condition can include many disorders, many of which react with the digestive tract resulting in chronic inflammation.
Both large and small intestines will swell and become irritated, which produces exceptional belly pain along with rectal bleeds and diarrhea plus symptoms that do not seem associated, including fever, fatigue, and joint pain.
While the symptoms could become stable, they can come back when there is a “flare-up.” Treatments recommended by the GI professional can be lifestyle changes, meds, or surgery.
Final Thought
A gastroenterologist will also perform preventative testing such as a colonoscopy as a preventative measure for colon cancer, endoscopy to look down the throat into the esophagus, and further for potential risks, with these often done at regular intervals to pay attention to growth which can occur over time.
Finding the growth and removing them prevents the instance of cancer. Early detection and a precise diagnosis will save a life. The recommendation is that all individuals have preventative testing beginning at 50 years of age, particularly for colon cancer.
The GI doctor plays the primary role in keeping cancer at bay for countless people since colon cancer is among the most common cancers. See here for those who want to get into the field.